Which of these statements about lymphocytes is false? This question delves into the fascinating realm of immunology, exploring the intricacies of lymphocytes, their multifaceted roles in the immune system, and the potential misconceptions surrounding their functions.
Lymphocytes, the cornerstone of our immune defense, are specialized cells that orchestrate intricate immune responses to protect us from a myriad of pathogens. Their remarkable diversity and adaptability enable them to recognize and eliminate foreign invaders with remarkable precision. However, amidst the wealth of knowledge about lymphocytes, certain misconceptions persist.
This discussion aims to clarify these misconceptions, providing a deeper understanding of these vital immune cells.
Definition of Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that play a critical role in the body’s immune system. They are responsible for recognizing and destroying foreign invaders, such as bacteria, viruses, and toxins.
Role of Lymphocytes in the Immune System
Lymphocytes are the main cells involved in the adaptive immune response, which is a highly specific and targeted defense mechanism that allows the body to tailor its response to specific pathogens.
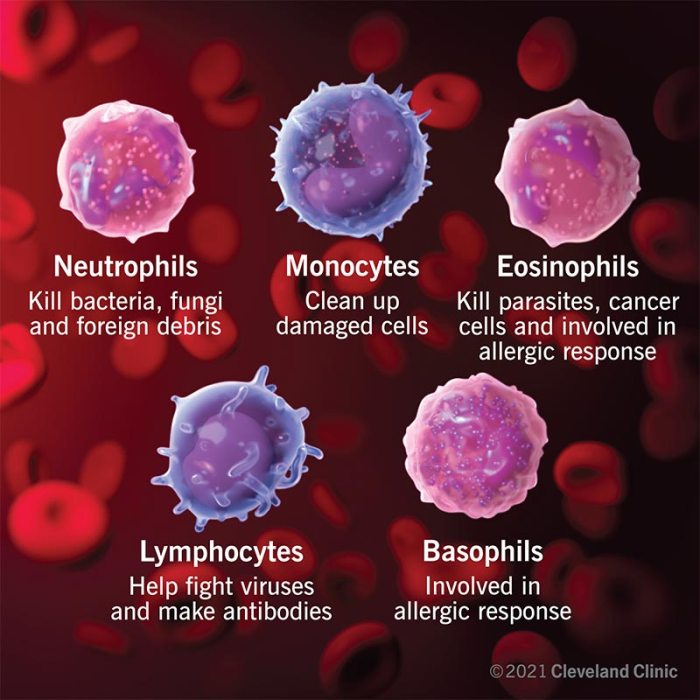
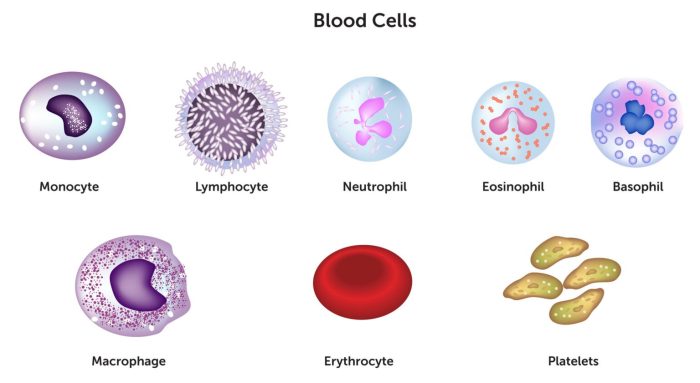
Different Types of Lymphocytes and Their Functions
- T lymphocytes (T cells):T cells are responsible for cell-mediated immunity, which involves the direct killing of infected cells or the release of cytokines that activate other immune cells.
- B lymphocytes (B cells):B cells are responsible for antibody-mediated immunity, which involves the production of antibodies that bind to and neutralize foreign invaders.
- Natural killer (NK) cells:NK cells are a type of innate immune cell that can kill infected cells and tumor cells.
Characteristics of Lymphocytes
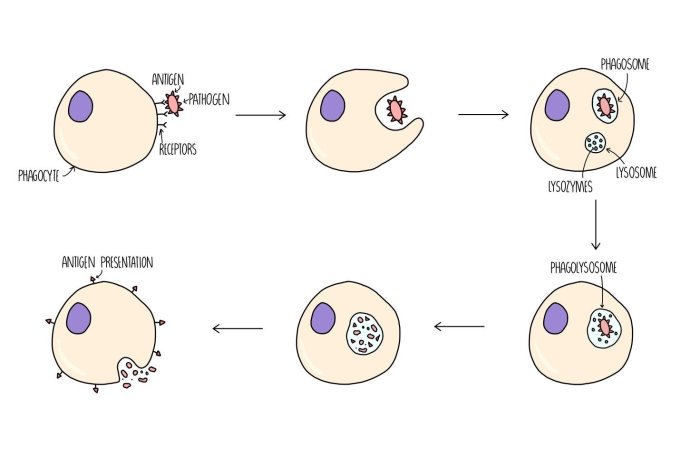
Structure and Morphology of Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes are small, round cells with a large nucleus and a small amount of cytoplasm. They have a variety of surface receptors that allow them to recognize specific antigens.
Lifespan and Circulation of Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes have a long lifespan, with some living for up to 10 years. They circulate throughout the body in the blood and lymph, and can migrate to sites of infection or inflammation.
Activation and Differentiation of Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes are activated when they encounter an antigen that they recognize. Once activated, they can differentiate into effector cells, which are cells that can directly attack foreign invaders, or memory cells, which can remember the antigen and provide a rapid response to future infections.
Functions of Lymphocytes
Involvement of Lymphocytes in Antibody-Mediated Immunity
B cells produce antibodies, which are proteins that bind to specific antigens. Once bound, antibodies can neutralize the antigen, prevent it from entering cells, or target it for destruction by other immune cells.
Role of Lymphocytes in Cell-Mediated Immunity
T cells kill infected cells by releasing cytotoxic molecules or by activating other immune cells, such as macrophages.
Examples of Lymphocyte Responses to Specific Pathogens
- Influenza virus:T cells kill infected cells, while B cells produce antibodies that neutralize the virus.
- Bacteria:B cells produce antibodies that neutralize bacteria, while T cells activate macrophages to kill the bacteria.
- Cancer cells:NK cells can kill cancer cells, while T cells can activate other immune cells to destroy the cancer cells.
Regulation of Lymphocyte Activity
Mechanisms that Regulate Lymphocyte Activation and Proliferation, Which of these statements about lymphocytes is false
The activity of lymphocytes is tightly regulated to prevent excessive immune responses or autoimmune disorders. This regulation is mediated by a variety of mechanisms, including:
- Co-stimulatory molecules:These molecules are expressed on the surface of antigen-presenting cells and help to activate T cells.
- Cytokines:These are proteins that can either activate or suppress lymphocyte activity.
- Regulatory T cells:These cells help to suppress immune responses and prevent autoimmune disorders.
FAQ: Which Of These Statements About Lymphocytes Is False
Are all lymphocytes T cells?
No, lymphocytes encompass both T cells and B cells, each with distinct roles in the immune response.
Can lymphocytes live forever?
No, lymphocytes have a finite lifespan, although memory cells can persist for extended periods.
Are lymphocytes only found in the blood?
No, lymphocytes circulate throughout the body, including the lymphatic system and various tissues.