Fe mno4 3 compound name – Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of FeMnO4 3, a compound that holds a treasure trove of intriguing properties and applications. From its fascinating molecular structure to its remarkable reactivity, FeMnO4 3 promises an exploration that will illuminate the intricacies of inorganic chemistry.
Prepare to unravel the secrets of this enigmatic compound, as we delve into its physical and chemical characteristics, dissect its molecular architecture, and uncover its potential in various fields, including water treatment, environmental remediation, and even energy storage.
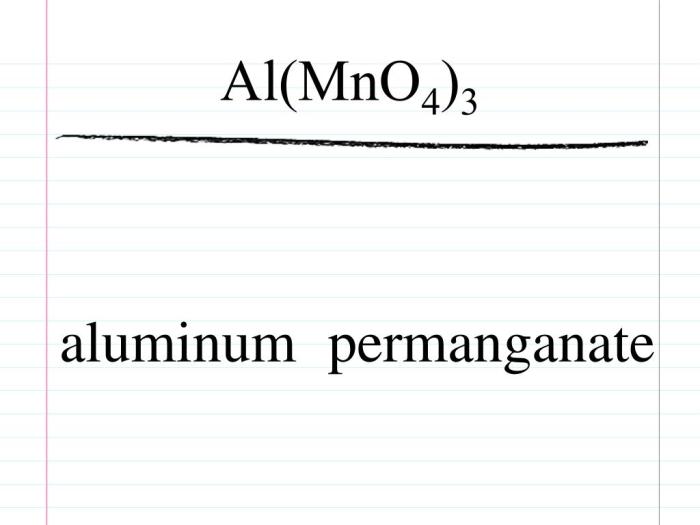
Compound Nomenclature
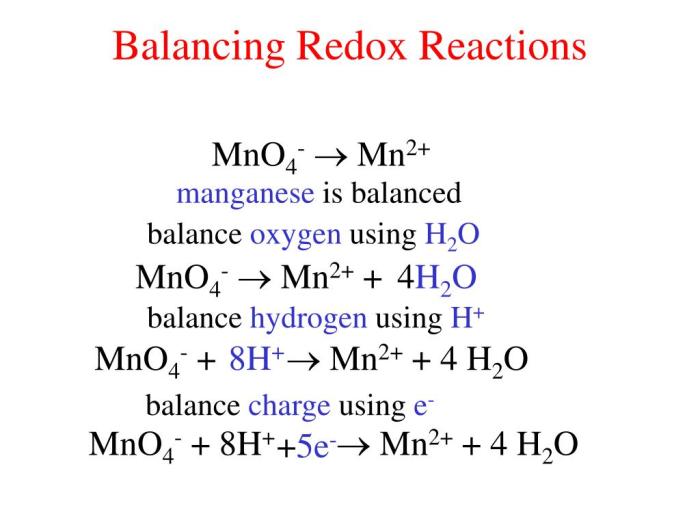
The systematic naming of inorganic compounds follows specific rules to ensure consistency and clarity in chemical communication. These rules are based on the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) guidelines.
Transition Metal Compounds
Transition metal compounds are named according to their oxidation state, which indicates the charge of the metal ion. The oxidation state is represented by a Roman numeral in parentheses after the metal name.
For example, Fe(II)Cl 2is iron(II) chloride, where Fe has an oxidation state of +2. Fe(III) 2O 3is iron(III) oxide, where Fe has an oxidation state of +3.
Compounds with Different Oxidation States
When a metal can exhibit multiple oxidation states, the oxidation state must be specified in the name. This is done using Roman numerals in parentheses after the metal name.
For example, copper(I) chloride is CuCl, while copper(II) chloride is CuCl 2. Similarly, tin(II) oxide is SnO, while tin(IV) oxide is SnO 2.
Properties of FeMnO4 3
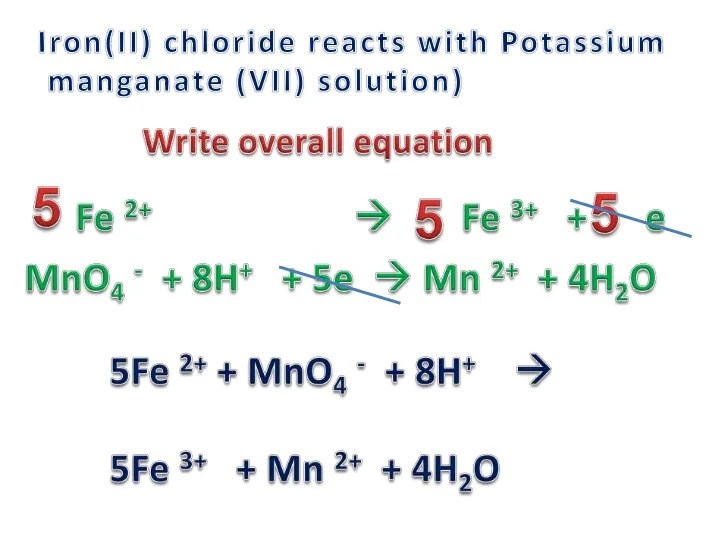
FeMnO4 3, also known as potassium permanganate, is a versatile chemical compound with unique physical and chemical properties. It is a strong oxidizing agent, exhibiting diverse applications in various industries and scientific fields.
Solubility
FeMnO4 3 is highly soluble in water. When dissolved, it dissociates into potassium ions (K+) and permanganate ions (MnO4-). The solubility of FeMnO4 3 increases with temperature, allowing for the preparation of concentrated solutions.
Color
One of the most striking properties of FeMnO4 3 is its intense purple color. The permanganate ion (MnO4-) absorbs light in the visible spectrum, giving rise to the characteristic coloration. The color of FeMnO4 3 solutions can vary from pale pink to deep purple, depending on the concentration.
Stability
FeMnO4 3 is a relatively stable compound, but it can decompose under certain conditions. It is sensitive to light, heat, and reducing agents. Exposure to these factors can cause the decomposition of FeMnO4 3, leading to the formation of manganese dioxide (MnO2) and other products.
Magnetic Properties
FeMnO4 3 exhibits paramagnetic behavior. Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism where the individual molecules of a substance have a permanent magnetic moment. In the case of FeMnO4 3, the magnetic moment arises from the unpaired electrons in the manganese ion (Mn7+).
Structure of FeMnO4 3: Fe Mno4 3 Compound Name
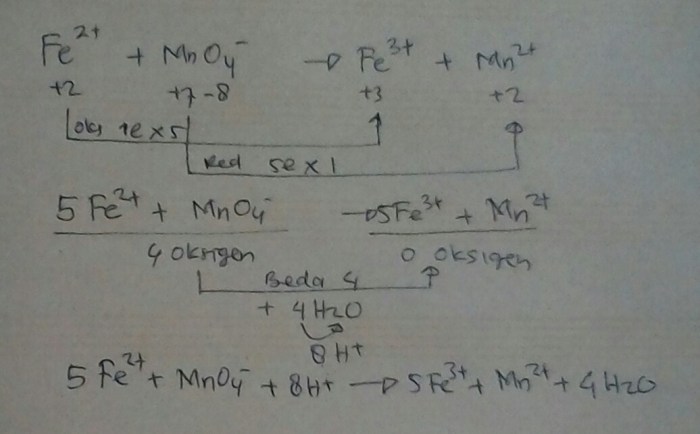
The molecular structure of FeMnO4 3 is characterized by a central iron(III) ion (Fe3+) surrounded by four manganate(VI) ions (MnO4-) in a tetrahedral arrangement.
Coordination Geometry and Oxidation States, Fe mno4 3 compound name
The coordination geometry around the iron(III) ion is tetrahedral, with the four manganate(VI) ions occupying the four corners of a tetrahedron. The iron(III) ion is in the +3 oxidation state, while the manganate(VI) ions are in the +6 oxidation state.
Bonding Interactions
The bonding within the FeMnO4 3 molecule is primarily ionic, with the iron(III) ion attracting the negatively charged manganate(VI) ions. However, there is also some covalent character to the bonds, due to the overlap of the d orbitals of the iron(III) ion with the p orbitals of the oxygen atoms in the manganate(VI) ions.
Reactivity of FeMnO4 3
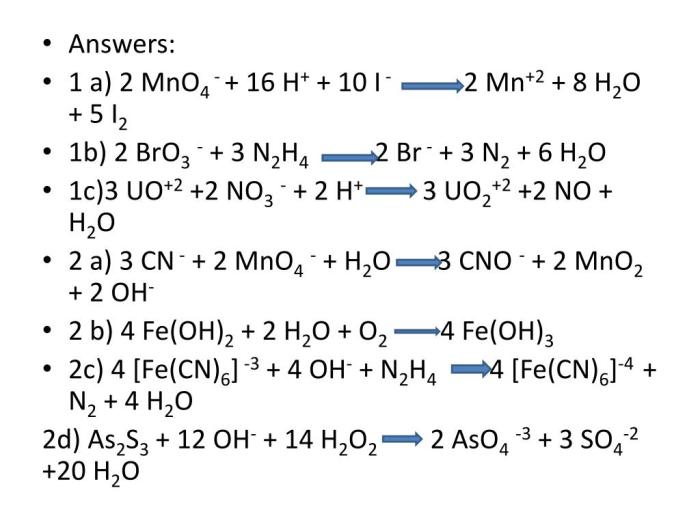
FeMnO4 3 is a strong oxidizing agent and undergoes redox reactions easily. It can oxidize a wide range of organic and inorganic compounds.
Fe mno4 3 is a chemical compound that is used as a strong oxidizing agent. It is commonly known as potassium permanganate and has a variety of applications, including as a disinfectant, deodorizer, and bleaching agent. What is s7 for 6-24+96 is a related topic that discusses the formula for calculating the value of s7 in the equation 6-24+96.
While the two topics are distinct, they share a common thread in that they both involve chemical calculations.
Redox Reactions of FeMnO4 3
In redox reactions, FeMnO4 3 can act as both an oxidizing agent and a reducing agent. When it acts as an oxidizing agent, it gets reduced to MnO2 or Mn2+ ions, and when it acts as a reducing agent, it gets oxidized to Fe2+ ions.
Oxidizing Properties of FeMnO4 3
As an oxidizing agent, FeMnO4 3 can oxidize:
- Alcohols to aldehydes or ketones
- Aldehydes to carboxylic acids
- Unsaturated hydrocarbons to epoxides or diols
- Sulfides to sulfates
- Iodides to iodine
Reducing Properties of FeMnO4 3
As a reducing agent, FeMnO4 3 can reduce:
- Permanganate ions (MnO4-) to manganese dioxide (MnO2)
- Dichromate ions (Cr2O72-) to chromium(III) ions (Cr3+)
- Iron(III) ions (Fe3+) to iron(II) ions (Fe2+)
Examples of Reactions Involving FeMnO4 3
Here are some examples of reactions involving FeMnO4 3:
- Oxidation of ethanol to acetaldehyde: 3 CH3CH2OH + 2 FeMnO4 3 + H2O → 3 CH3CHO + 2 Fe(OH)3 + 2 MnO2
- Oxidation of iodide ions to iodine: 2 KI + 2 FeMnO4 3 + 8 H2SO4 → I2 + 2 Fe2(SO4)3 + 2 MnSO4 + 8 H2O
- Reduction of permanganate ions to manganese dioxide: 2 KMnO4 + 3 H2SO4 + 5 FeSO4 → K2SO4 + 2 MnSO4 + 3 Fe2(SO4)3 + 8 H2O
Applications of FeMnO4 3
FeMnO4 3 has a wide range of industrial applications due to its unique properties and versatility. It is primarily used as an oxidizing agent in various processes, as well as in water treatment and environmental remediation.
Industrial Applications
- Bleaching Agent:FeMnO4 3 is employed as a bleaching agent in the textile industry to remove color from fabrics and textiles. It is particularly effective in bleaching cotton and other natural fibers.
- Oxidizing Agent:FeMnO4 3 is used as an oxidizing agent in a variety of chemical reactions. For example, it is used in the production of dyes, pigments, and other chemicals.
- Water Treatment:FeMnO4 3 is used in water treatment to remove impurities and contaminants. It is particularly effective in removing heavy metals, such as lead and mercury, from water.
- Environmental Remediation:FeMnO4 3 is used in environmental remediation to clean up contaminated soil and groundwater. It is effective in breaking down pollutants, such as oil and gasoline, into harmless substances.
Energy Storage and Catalysis
In addition to its industrial applications, FeMnO4 3 has potential applications in energy storage and catalysis. It is being investigated as a cathode material in lithium-ion batteries and as a catalyst for various chemical reactions.
- Energy Storage:FeMnO4 3 is a promising candidate for use as a cathode material in lithium-ion batteries due to its high energy density and stability.
- Catalysis:FeMnO4 3 has been shown to be an effective catalyst for a variety of chemical reactions, including the decomposition of organic compounds and the reduction of nitrogen oxides.
FAQ Explained
What is the molecular weight of FeMnO4 3?
169.81 g/mol
What is the color of FeMnO4 3?
Dark green
Is FeMnO4 3 soluble in water?
Yes
What is the oxidation state of manganese in FeMnO4 3?
+6
What is the oxidation state of iron in FeMnO4 3?
+3