Which of the following is correct regarding the viral envelope? This question takes center stage as we delve into the fascinating world of viruses, their intricate structures, and the mechanisms they employ to infect host cells. In this comprehensive exploration, we will unravel the composition and structure of the viral envelope, examining its role in viral entry and immune evasion.
Furthermore, we will investigate the potential of targeting the viral envelope for antiviral therapies, providing a deeper understanding of this crucial aspect of virology.
The viral envelope, a defining feature of certain viruses, plays a pivotal role in their infectivity and survival. Composed of a lipid bilayer derived from the host cell membrane and embedded viral proteins, the envelope serves as a protective barrier and a gateway for viral entry into host cells.
Understanding the intricacies of the viral envelope is essential for developing effective antiviral strategies and combating viral infections.
Viral Envelope

The viral envelope is a crucial structure found in some viruses, playing a vital role in viral entry, immune evasion, and viral evolution. It is composed of a lipid bilayer derived from the host cell membrane and embedded viral proteins.
The lipid bilayer provides a protective barrier for the viral genome, while the viral proteins facilitate interactions with host cells and mediate viral entry.
Composition and Structure, Which of the following is correct regarding the viral envelope
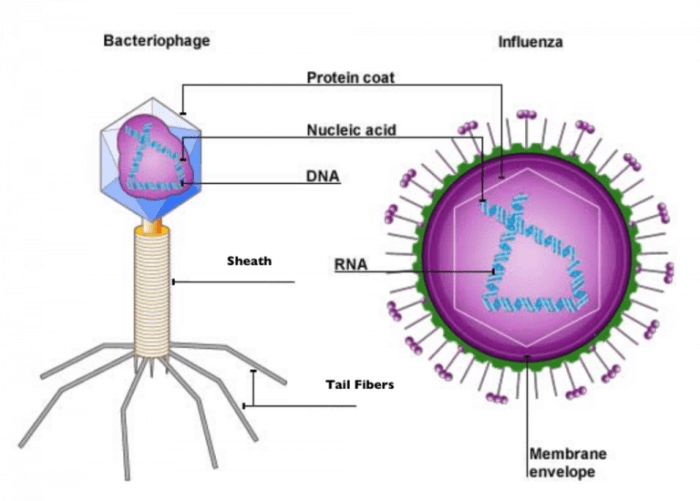
The viral envelope is composed of a lipid bilayer that encloses the viral nucleocapsid. The lipid bilayer is derived from the host cell membrane during viral budding, and it contains various lipids, including phospholipids, cholesterol, and glycolipids. Embedded within the lipid bilayer are viral proteins, which are responsible for viral attachment to host cells, membrane fusion, and immune evasion.
The viral proteins can be highly glycosylated, forming viral glycoproteins that interact with specific receptors on the host cell surface.
Role in Viral Entry
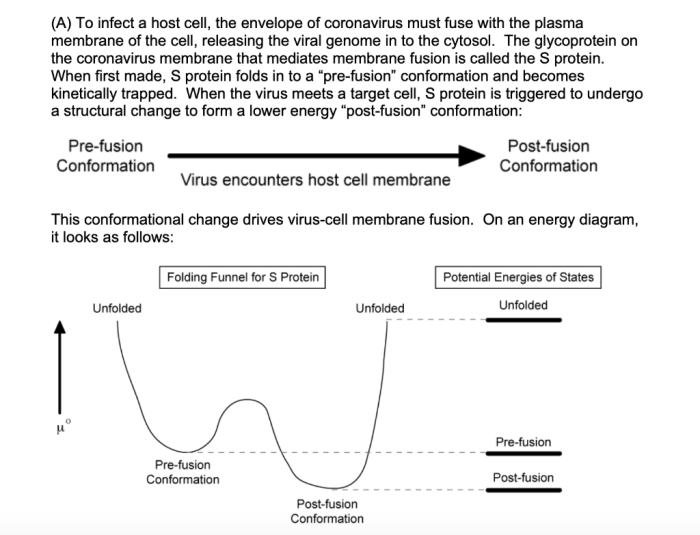
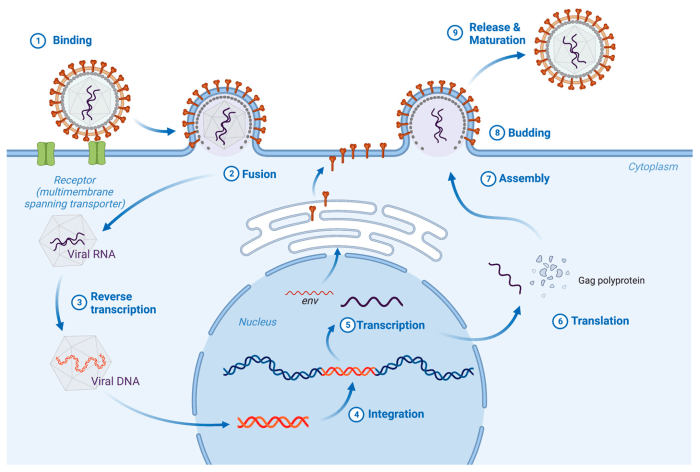
The viral envelope plays a critical role in viral entry into host cells. The viral glycoproteins bind to specific receptors on the host cell surface, triggering a conformational change in the viral envelope that leads to membrane fusion. This fusion allows the viral nucleocapsid to be released into the host cell cytoplasm, where it can initiate viral replication.
Some viruses, such as HIV and influenza, utilize the viral envelope for entry into host cells.
Immune Evasion
The viral envelope can also help viruses evade the host immune response. The viral glycoproteins are highly variable, allowing the virus to escape recognition by the host immune system. Additionally, the viral envelope can shield the viral nucleocapsid from antibodies and other immune effector molecules.
This immune evasion allows the virus to establish infection and replicate within the host.
Antiviral Targets
The viral envelope is a potential target for antiviral therapies. Antiviral drugs can be designed to inhibit viral entry by blocking the interaction between viral glycoproteins and host cell receptors. Other drugs can disrupt the viral envelope structure, preventing membrane fusion and viral entry.
Antiviral drugs that target the viral envelope include oseltamivir (Tamiflu) for influenza and enfuvirtide (Fuzeon) for HIV.
Evolution and Variability
The viral envelope can contribute to viral evolution and variability. The viral glycoproteins are subject to mutations, which can lead to changes in the virus’s ability to infect host cells and evade the immune system. This variability can drive viral evolution and the emergence of new viral strains.
For example, the influenza virus undergoes antigenic drift and shift due to mutations in the viral glycoproteins, leading to the emergence of new strains that can evade existing immunity.
Essential Questionnaire: Which Of The Following Is Correct Regarding The Viral Envelope
What is the function of the viral envelope?
The viral envelope serves multiple functions, including protecting the viral genome from degradation, facilitating viral entry into host cells, and aiding in immune evasion.
How does the viral envelope contribute to viral entry?
The viral envelope contains specific proteins that bind to receptors on the surface of host cells. This binding triggers a fusion process, allowing the viral envelope to merge with the host cell membrane and release the viral genome into the host cell.
How does the viral envelope help viruses evade the immune system?
The viral envelope can display glycoproteins that mimic host cell molecules, making it difficult for the immune system to recognize and target the virus. Additionally, the envelope can shield viral antigens from immune surveillance.