Macro topic 2.1 the circular flow and gdp – Macro Topic 2.1: The Circular Flow and GDP provides a comprehensive overview of the fundamental concepts that drive economic activity. This topic explores the intricate relationship between households, firms, and the government, highlighting their roles in the circular flow of income and expenditure.
Furthermore, it delves into the measurement of Gross Domestic Product (GDP), examining its components and significance as a key indicator of economic performance.
The circular flow model depicts the continuous exchange of goods and services between households and firms, facilitated by the government’s role in taxation and spending. GDP, calculated using various methods, serves as a comprehensive measure of the total value of goods and services produced within a country’s borders.
Understanding the interplay between the circular flow and GDP is crucial for grasping the dynamics of economic growth and stability.
The Circular Flow of Economic Activity: Macro Topic 2.1 The Circular Flow And Gdp
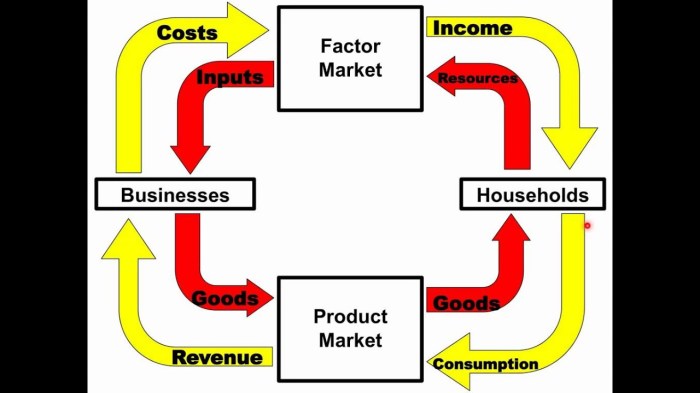
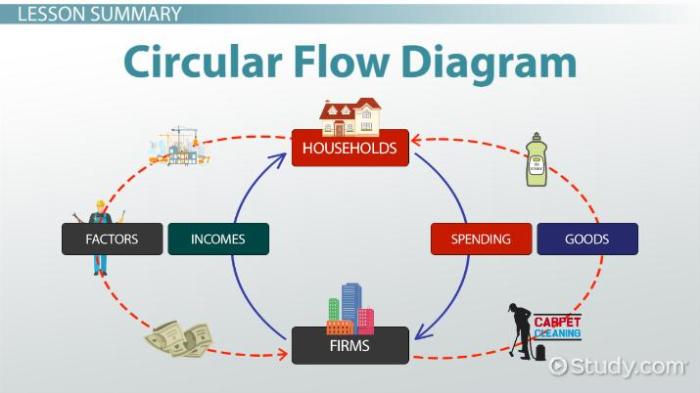
The circular flow model is a simplified representation of the economy that shows the flow of goods and services between households, firms, and the government. Households provide labor and other resources to firms, which use these resources to produce goods and services.
Firms then sell these goods and services to households, which use them to satisfy their wants and needs. The government collects taxes from households and firms and uses these taxes to provide public goods and services.
The circular flow model is a useful tool for understanding how the economy works. It can be used to analyze the impact of different economic policies, such as changes in taxes or government spending.
Role of Households, Firms, and the Government in the Circular Flow
- Households provide labor and other resources to firms.
- Firms use these resources to produce goods and services.
- Firms then sell these goods and services to households.
- Households use these goods and services to satisfy their wants and needs.
- The government collects taxes from households and firms.
- The government uses these taxes to provide public goods and services.
Diagram of the Circular Flow Model
The circular flow model can be represented by a diagram. The diagram shows the flow of goods and services between households, firms, and the government. The diagram also shows the flow of money between these three sectors.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a measure of the total value of all goods and services produced in a country in a given period of time. GDP is a widely used measure of economic growth and is often used to compare the economic performance of different countries.
Components of GDP
GDP is calculated by adding up the value of all goods and services produced in a country in a given period of time. The components of GDP include:
- Consumption
- Investment
- Government spending
- Exports
- Imports
Methods of Calculating GDP
There are three main methods of calculating GDP:
- The expenditure approach
- The income approach
- The value-added approach
Table Comparing the GDP of Different Countries
| Country | GDP (2022) |
|---|---|
| United States | $26.49 trillion |
| China | $18.32 trillion |
| Japan | $4.93 trillion |
| Germany | $4.22 trillion |
| United Kingdom | $3.22 trillion |
The Relationship between the Circular Flow and GDP

The circular flow model and GDP are closely related. GDP is a measure of the total value of all goods and services produced in a country in a given period of time. The circular flow model shows how goods and services flow between households, firms, and the government.
The circular flow model can be used to understand how changes in one sector of the economy can affect GDP.
How the Circular Flow Model is Related to GDP, Macro topic 2.1 the circular flow and gdp
The circular flow model is related to GDP in the following ways:
- GDP is a measure of the total value of all goods and services produced in a country in a given period of time.
- The circular flow model shows how goods and services flow between households, firms, and the government.
- The circular flow model can be used to understand how changes in one sector of the economy can affect GDP.
How Changes in the Circular Flow Can Affect GDP
Changes in the circular flow can affect GDP in the following ways:
- An increase in consumption will lead to an increase in GDP.
- An increase in investment will lead to an increase in GDP.
- An increase in government spending will lead to an increase in GDP.
- An increase in exports will lead to an increase in GDP.
- An increase in imports will lead to a decrease in GDP.
Example of How a Change in Consumer Spending Can Affect GDP
An example of how a change in consumer spending can affect GDP is the following:
If consumers decide to spend more money on cars, this will lead to an increase in demand for cars. This will lead to an increase in production of cars, which will lead to an increase in GDP.
Limitations of GDP
GDP is a useful measure of economic growth, but it has some limitations. GDP does not measure the following:
- The distribution of income
- The quality of life
- The environmental impact of economic activity
Alternative Measures of Economic Well-being
There are a number of alternative measures of economic well-being that can be used to supplement GDP. These measures include:
- The Human Development Index
- The Genuine Progress Indicator
- The Index of Sustainable Economic Welfare
Table Comparing GDP with Other Measures of Economic Well-being
| Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| GDP | The total value of all goods and services produced in a country in a given period of time. |
| Human Development Index | A measure of the average achievements in a country in three basic dimensions of human development: a long and healthy life, knowledge, and a decent standard of living. |
| Genuine Progress Indicator | A measure of economic progress that takes into account the environmental impact of economic activity. |
| Index of Sustainable Economic Welfare | A measure of economic well-being that takes into account the distribution of income, the quality of life, and the environmental impact of economic activity. |
Clarifying Questions
What is the circular flow model?
The circular flow model is a simplified representation of the economy that shows the flow of goods, services, and money between households, firms, and the government.
How is GDP calculated?
GDP can be calculated using three main methods: the expenditure approach, the income approach, and the value-added approach.
What are the limitations of GDP?
GDP is a useful measure of economic activity, but it has some limitations. For example, GDP does not measure non-market activities, such as housework or volunteer work.