Navigating the body muscular system 1 – Navigating the body’s muscular system 1 is a journey that unravels the intricate workings of our bodies. Muscles, the engines of movement, play a pivotal role in our overall health and well-being, shaping our posture, facilitating movement, and supporting vital bodily functions.
Delving into the depths of the muscular system, we embark on a quest to uncover its complexities, unravel its functions, and appreciate its profound impact on our lives.
Our exploration begins with an in-depth examination of the diverse types of muscles that orchestrate our movements, from the striated skeletal muscles to the smooth muscles lining our organs and the tireless cardiac muscle that powers our hearts. We delve into the intricate structure and function of muscle fibers, unraveling the mysteries of myofibrils, sarcomeres, and the neuromuscular junction.
Introduction
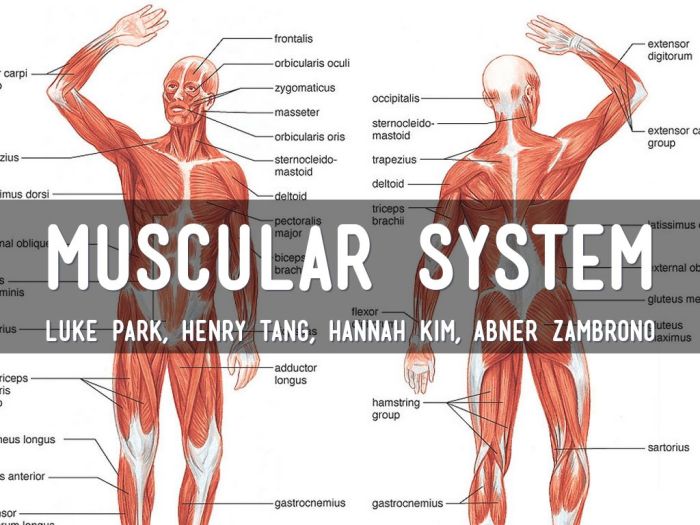
Understanding the body’s muscular system is crucial for comprehending human movement, posture, and overall health. Muscles play a vital role in enabling physical activities, maintaining structural integrity, and supporting bodily functions.
This article provides a comprehensive exploration of the muscular system, covering its various types, structure, function, interactions with other body systems, and implications for health, fitness, and exercise performance.
Types of Muscles
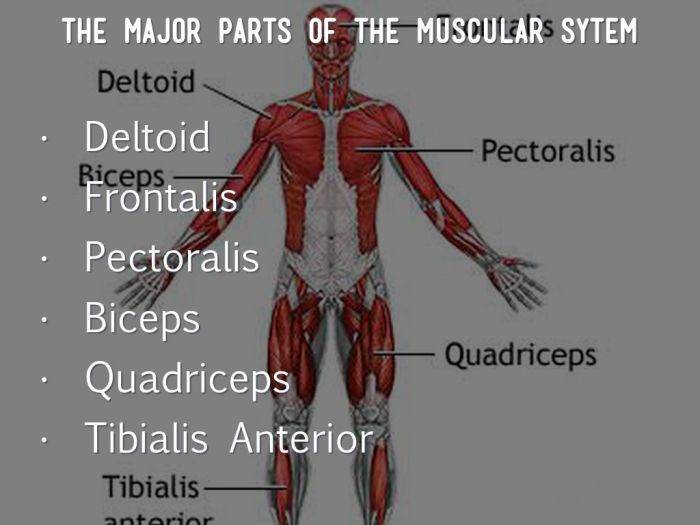
The human body comprises three main types of muscles:
- Skeletal muscles: Voluntary muscles attached to bones, responsible for conscious movements.
- Smooth muscles: Involuntary muscles found in internal organs, blood vessels, and respiratory tract, controlling involuntary functions.
- Cardiac muscles: Involuntary muscles found exclusively in the heart, responsible for pumping blood throughout the body.
Structure and Function of Muscles
Muscle fibers, the basic units of muscles, contain myofibrils and sarcomeres, the contractile units. Muscle contraction occurs through the sliding filament mechanism, where actin and myosin filaments interact, shortening the muscle fiber.
Muscle relaxation involves the breakdown of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and the detachment of myosin heads from actin filaments.
Major Muscle Groups: Navigating The Body Muscular System 1
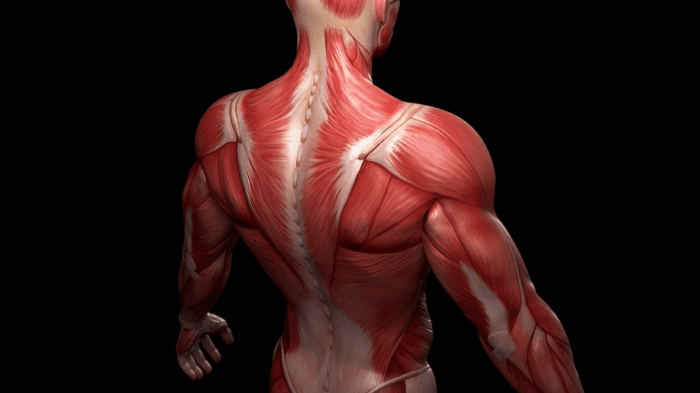
The body’s muscles are organized into distinct groups based on their location and function. Major muscle groups include:
- Head and Neck: Muscles of facial expression, mastication, and neck movements.
- Trunk: Muscles of the chest, back, abdomen, and pelvic floor.
- Upper Limbs: Muscles of the shoulders, arms, forearms, and hands.
- Lower Limbs: Muscles of the thighs, legs, and feet.
Interactions with Other Body Systems
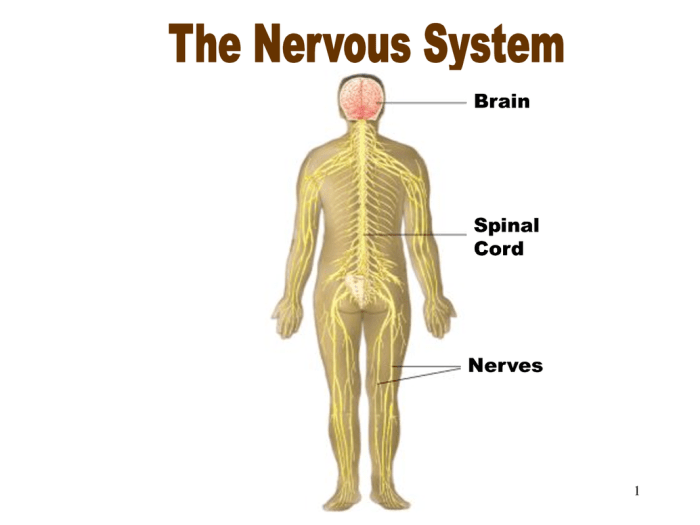
Muscles interact closely with the skeletal system, providing movement and stability. They also interface with the nervous system, receiving signals from the brain and spinal cord to contract and relax.
Furthermore, muscles play a crucial role in the circulatory system, aiding in blood flow and regulating blood pressure.
Quick FAQs
What are the different types of muscles?
There are three main types of muscles: skeletal muscles, smooth muscles, and cardiac muscles.
What is the function of skeletal muscles?
Skeletal muscles are responsible for voluntary movement, such as walking, running, and lifting objects.
What is the function of smooth muscles?
Smooth muscles are responsible for involuntary movements, such as digestion and blood flow.
What is the function of cardiac muscles?
Cardiac muscles are responsible for the pumping action of the heart.