Welcome to the fascinating world of DNA analysis, where the Gizmo DNA Analysis Answer Key serves as your guide to unlocking the mysteries of life. Prepare to embark on a captivating journey into the realm of genetics, where we unravel the secrets encoded within the very building blocks of our existence.
As we delve into the complexities of DNA structure and function, you’ll gain a profound understanding of how genetic information is stored, transmitted, and varies among individuals and species. We’ll explore the cutting-edge techniques used to extract, amplify, sequence, and analyze DNA, empowering you with knowledge that spans a wide range of scientific disciplines.
Gizmo DNA Analysis Overview
Gizmo DNA Analysis is a virtual laboratory that allows students to explore the principles and techniques of DNA analysis. Through hands-on simulations, students can learn about the structure of DNA, DNA replication, and DNA fingerprinting.
DNA analysis is a powerful tool that has revolutionized the fields of biology and medicine. By understanding the structure and function of DNA, scientists have been able to develop new treatments for diseases, identify criminals, and even trace our evolutionary history.
The Gizmo DNA Analysis Answer Key provides a detailed explanation of the steps involved in analyzing DNA sequences. The key includes information on how to identify genes, determine the sequence of amino acids, and predict the structure of proteins. To learn more about the role of women in science, you can check out the angels of truth kappa delta website.
The Gizmo DNA Analysis Answer Key is an invaluable resource for students and teachers alike, and it can help you gain a deeper understanding of the complexities of DNA.
Key Concepts and Principles
- DNA is a molecule that contains the instructions for an organism’s development and characteristics.
- DNA is made up of four different nucleotides: adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine.
- The sequence of nucleotides in DNA determines the genetic code for an organism.
- DNA replication is the process by which DNA makes a copy of itself.
- DNA fingerprinting is a technique that can be used to identify individuals by their unique DNA patterns.
Steps Involved in Gizmo DNA Analysis Simulation
- Extract DNA from a sample.
- Amplify the DNA using PCR.
- Analyze the DNA using gel electrophoresis.
- Interpret the results of the DNA analysis.
DNA Structure and Function
DNA, the molecule of heredity, carries the instructions for an organism’s development and characteristics. It is a complex molecule composed of nucleotides, which are made up of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
There are four different types of nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). These bases pair up with each other to form base pairs, which are the building blocks of DNA. Adenine always pairs with thymine, and cytosine always pairs with guanine.
The sequence of base pairs in a DNA molecule determines the genetic information that is passed from one generation to the next. This information is used to build proteins, which are the building blocks of cells and tissues.
Variations in DNA Sequences
DNA sequences can vary between individuals and species. These variations are responsible for the diversity of life on Earth. For example, the DNA sequence of a human is about 99% identical to the DNA sequence of a chimpanzee. However, the remaining 1% difference accounts for the many differences between humans and chimpanzees.
DNA Extraction and Amplification
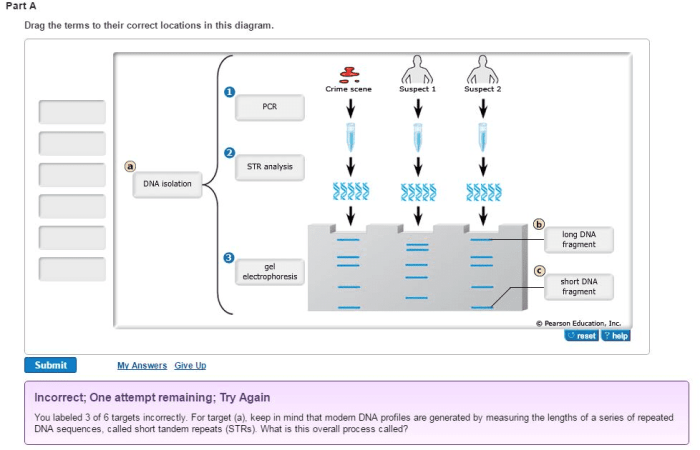
DNA extraction and amplification are crucial techniques used to isolate and make copies of DNA, providing the foundation for various applications in research, forensics, and medicine.
DNA Extraction
DNA extraction involves isolating DNA from cells. Methods include mechanical, chemical, and enzymatic techniques. Mechanical methods use force to break open cells, while chemical methods employ detergents and enzymes to dissolve cell membranes and release DNA. Enzymatic methods utilize specific enzymes, such as proteases and nucleases, to digest proteins and other cellular components, leaving purified DNA.
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
PCR is a molecular biology technique used to amplify specific DNA sequences. It involves multiple cycles of heating and cooling to separate and copy DNA strands. During each cycle, a thermostable DNA polymerase enzyme adds complementary nucleotides to the single-stranded DNA templates, resulting in exponential amplification of the target DNA sequence.
Importance of DNA Extraction and Amplification
DNA extraction and amplification are essential for various fields:
- Medical diagnostics:Identifying genetic disorders, detecting pathogens, and personalized medicine.
- Forensics:DNA fingerprinting for identification, paternity testing, and crime scene investigation.
- Genetic research:Studying gene expression, mutations, and genetic diversity.
- Biotechnology:Cloning genes, producing recombinant proteins, and developing genetically modified organisms.
DNA Sequencing and Analysis
DNA sequencing determines the order of nucleotides in a DNA molecule. It’s crucial for understanding gene structure, identifying mutations, and studying genetic variation.
Sanger Sequencing
Sanger sequencing, also known as dideoxy sequencing, is a widely used technique for DNA sequencing. It involves using a primer to initiate DNA synthesis and a mixture of normal nucleotides and dideoxynucleotides (ddNTPs). DdNTPs lack a 3′-OH group, so they terminate DNA synthesis when incorporated into the growing strand.
By separating the fragments based on their length using electrophoresis, the sequence of the DNA can be determined.
Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
NGS technologies, such as Illumina sequencing and Ion Torrent sequencing, are high-throughput methods that can sequence millions of DNA fragments simultaneously. NGS involves fragmenting the DNA, ligating adapters, and amplifying the fragments using PCR. The amplified fragments are then sequenced, and the data is assembled to reconstruct the original DNA sequence.
DNA Sequence Analysis
Once the DNA sequence is obtained, it can be analyzed to identify genes, mutations, and other genetic variations. Gene prediction algorithms search for open reading frames (ORFs) and other features characteristic of genes. Mutations can be identified by comparing the sequence to a reference genome or by looking for changes that disrupt gene function.
Applications of DNA Sequencing
DNA sequencing has wide-ranging applications in various fields:
- Medicine:Identifying genetic variants associated with diseases, developing personalized treatments, and diagnosing genetic disorders.
- Forensics:Identifying individuals from DNA samples, establishing paternity, and solving crimes.
- Evolutionary biology:Studying genetic diversity, tracing evolutionary relationships, and understanding the genetic basis of adaptation.
Applications of DNA Analysis
DNA analysis has revolutionized various fields by providing insights into the genetic makeup of individuals and species. Its applications extend from medicine and forensics to evolutionary biology.
Medicine
- Disease diagnosis:DNA analysis can identify genetic mutations and variations associated with specific diseases, enabling early diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.
- Personalized medicine:By analyzing an individual’s DNA, doctors can tailor treatments to their specific genetic profile, optimizing drug selection and dosage.
Forensics, Gizmo dna analysis answer key
- Crime scene investigation:DNA analysis of blood, hair, or other biological samples can link suspects to crime scenes or exonerate the innocent.
- Paternity testing:DNA analysis can determine the biological father of a child by comparing the DNA of the child, mother, and alleged father.
Evolutionary biology
- Studying genetic relationships:DNA analysis allows scientists to trace the genetic lineage of species, uncovering evolutionary relationships and patterns of biodiversity.
- Understanding genetic diversity:DNA analysis helps identify and conserve genetic diversity within populations, ensuring the resilience and adaptability of species.
Ethical Considerations in DNA Analysis
The rapid advancements in DNA analysis have brought immense benefits, but they also raise important ethical concerns. These concerns revolve around the privacy of genetic information, the potential for genetic discrimination, and the misuse of genetic data.
Privacy Concerns
DNA analysis can reveal highly personal information about an individual, including their genetic predispositions to certain diseases, their ancestry, and even their personality traits. This information can be used to identify individuals, track their movements, and even predict their future health outcomes.
The privacy of genetic information is therefore a major ethical concern.
Genetic Discrimination
Genetic discrimination occurs when individuals are treated differently based on their genetic makeup. This could include being denied health insurance, employment, or even housing based on the results of a DNA test. Genetic discrimination is a serious ethical concern because it can have a devastating impact on individuals and their families.
Misuse of Genetic Information
Genetic information can also be misused for malicious purposes, such as blackmail, identity theft, or even genetic engineering. The misuse of genetic information is a serious ethical concern because it can have far-reaching consequences for individuals and society as a whole.
Guidelines and Regulations
In order to address these ethical concerns, guidelines and regulations have been developed to ensure the responsible and ethical use of DNA analysis. These guidelines and regulations typically include provisions for:
- Informed consent: Individuals must be informed about the potential risks and benefits of DNA analysis before they consent to it.
- Data security: Genetic information must be stored and transmitted securely to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Privacy protections: Individuals have the right to control access to their genetic information and to prevent it from being used for discriminatory purposes.
FAQ: Gizmo Dna Analysis Answer Key
What is the purpose of the Gizmo DNA Analysis simulation?
The Gizmo DNA Analysis simulation provides a virtual environment for students to explore the principles and techniques of DNA analysis, allowing them to visualize and manipulate DNA sequences.
How does DNA store genetic information?
DNA stores genetic information in the sequence of its nucleotides, which are arranged in a specific order to form genes. Genes provide the instructions for building and maintaining an organism.
What is the role of PCR in DNA analysis?
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is a technique used to amplify DNA samples, creating multiple copies of a specific DNA sequence for further analysis.